Heat Shrink Wrapping Machines: An Efficient Packaging Solution for Modern Industries
In today’s fast-paced industrial production, product packaging not only impacts brand image but also directly influences logistics efficiency and cost control. As a highly efficient and flexible packaging solution, heat shrink wrapping machines have become essential equipment in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and electronics, thanks to their unique technical advantages. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of this modern packaging technology, covering its working principles, applications, technical strengths, and selection guidelines.
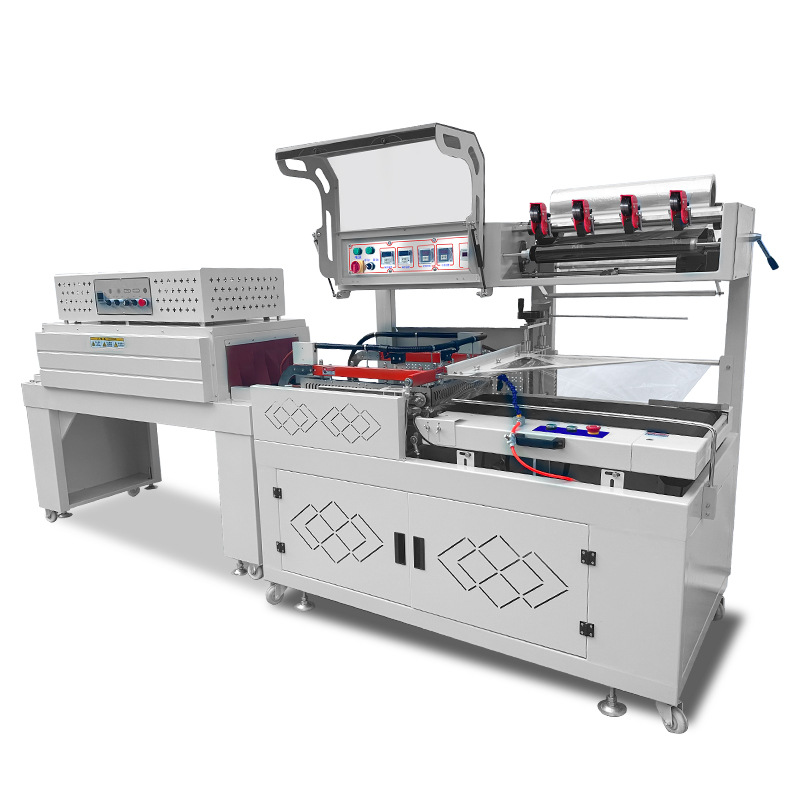
1. Working Principle and Core Components
The core mechanism of a heat shrink wrapping machine lies in utilizing the shrinkage properties of thermoplastic films when heated, which tightly envelop and conform to products. The workflow consists of three stages:
-
Film Wrapping Phase
Products enter the packaging area via a conveyor belt, where heat-shrinkable films (e.g., POF, PVC, or PE materials) are automatically draped over the items through a roller system, forming a loose wrap. Advanced models feature automatic film-cutting and sealing mechanisms for unmanned operations. -
Heating and Shrinkage
The wrapped products move into a heat tunnel, where hot air circulation, infrared radiation, or steam heating triggers uniform shrinkage of the film at 120–200°C, molding it tightly around the product’s contours. This process typically lasts 2–10 seconds, depending on film thickness and product geometry. -
Cooling and Solidification
The shrunk packaging is rapidly cooled via natural airflow or forced-air systems to stabilize the protective layer, ensuring durability during transportation.
Key components include a film frame system, conveyor belts, temperature control modules, and an intelligent control system. High-end models integrate PLC controllers and touchscreen interfaces for real-time parameter adjustments (e.g., temperature, speed) and self-diagnostic capabilities.
2. Applications: Versatility Across Industries
-
Food and Beverage
Used for multi-packaging beverage bottles, snack bundles, and fresh produce sealing, heat shrink wrapping enhances visual appeal while blocking oxygen and moisture. For example, POF film-wrapped 6-pack water bottles exhibit 50% higher drop resistance. -
Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Ensures dustproof and moisture-resistant packaging for medicine boxes, sanitized cotton swabs, and shampoo bottles, complying with GMP standards. Films can be printed with batch numbers and expiration dates for traceability. -
Electronics Manufacturing
Anti-static films protect delicate components like smartphone accessories and circuit boards from abrasion and electrostatic damage. A leading smartphone brand tripled packaging efficiency after adopting automated heat shrink lines. -
Publishing and Construction Materials
Plastic-wrapped books prevent staining, while bundled tiles and panels reduce transit damage. Construction companies report less than 0.3% logistics breakage rates with shrink-wrapped materials.
3. Technical Advantages: Efficiency Meets Sustainability
Compared to traditional packaging, heat shrink technology offers:
- High Speed and Energy Savings: Automated models achieve 60 packs/minute, cutting energy use by 40% versus conventional ovens. One beverage plant saved over 200,000 yuan annually post-upgrade.
- Enhanced Protection: Shrink-wrapped products withstand 3-meter drop tests, with compressive strength increasing by 70%—ideal for e-commerce logistics.
- Cost Efficiency: Film consumption is 35% lower than cardboard, and machines occupy 1/3 the space of traditional packaging lines.
- Eco-Friendliness: Biodegradable films (e.g., PLA) reduce packaging waste by 60%, aligning with global plastic reduction mandates.
4. Selection Guide: Aligning Machine with Needs
Key considerations for purchasing:
-
Product Specifications
Lightweight items (e.g., cosmetics) suit sleeve-style wrappers, while palletized goods require L-shaped sealers with 1.5m-wide tunnels. Irregularly shaped products need adjustable airflow nozzles. -
Production Volume
Choose manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic models based on output. Low-volume operations (under 2,000 units/day) may opt for desktop machines, whereas high-speed lines demand synchronized conveyor systems. -
Smart Features
Prioritize IoT-enabled machines with remote monitoring and data analytics. A multinational firm reduced packaging failures by 90% using connected devices. -
Energy and Maintenance
Infrared heating suits precision tasks; hot air systems are cost-effective. Modular designs enable component replacement in 15 minutes.
5. Future Trends: Intelligence and Sustainability
The evolution of heat shrink technology focuses on:
-
Smart Automation
5G-enabled predictive maintenance and AI vision systems auto-adjust parameters. A German manufacturer offers self-learning machines that optimize packaging strategies. -
Green Innovation
Bio-based shrink films now cost 1.2x traditional materials, while PE film recycling rates hit 85%. EU regulations mandate 30% recycled content in shrink films by 2023. -
Multifunctional Integration
Next-gen machines combine labeling, weighing, and metal detection. Japan’s “packaging robots” handle 200+ product types in unified workstations.